最小表示法¶
算法¶
字符串的最小表示法(Minimum Representation)通常指的是将字符串旋转至某个位置后,得到的所有可能字符串中字典序最小的一个。对于字符串S,其最小表示法可以通过以下步骤找到:
-
将字符串
S自身连接一次,形成新字符串S+S。 -
在
S+S中找到从任意位置i开始,长度等于原字符串长度的子串,该子串应满足它是所有这样的子串中字典序最小的。 具体算法步骤如下: -
初始化两个指针
i和j,分别指向S+S的开始位置,即i = 0和j = 1。 -
计算两个指针分别指向的子串的长度
n(原字符串的长度)。 -
比较两个指针指向的子串,如果
S[i:i+n]大于S[j:j+n],则将i更新为i + n和j中的较小值;否则,将j更新为j + n和i中的较小值。 -
重复步骤3,直到
i和j相等,此时i(或j)的位置就是最小表示法开始的位置。 -
最小表示法即为
S[i:i+n]。
例题 #1 Necklace¶
题目描述
有一天,袁同学绵了一条价值连城宝石项链,但是,一个严重的问题是,他竟然忘记了项链的主人是谁!在得知此事后,很多人向同学发来了很多邮件,都说项链是自己的,要求他归还(显然其中最多只有一个人说了真话)。袁同学要求每个人都写了一段关于自己项链的描述:
项链上的宝石用数字 \(0\) 至 \(9\) 来表示。一个对于项链的表示就是从项链的某个宝石开始:顺指针绕一圈,沿途记下经过的宝石,比如如下项链:
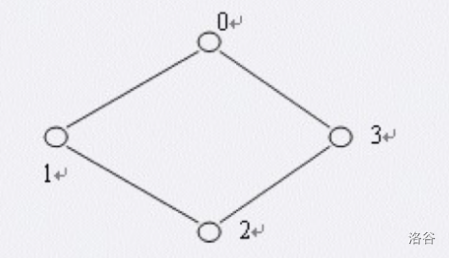
它的可能的四种表示是 \(0123\)、\(1230\)、\(2301\)、\(3012\)。
袁同学现在心急如焚,于是他找到了你,希望你能够编一个程序,判断两个给定的描述是否代表同一个项链(注意,项链是不会翻转的)。
输入格式
输入文件只有两行,每行一个由 \(0\) 至 \(9\) 组成的字符串,描述一个项链的表示(保证项链的长度是相等的)。
输出格式
如果两条项链不可能同构,那么输出 No,否则的话,第一行输出一个 Yes 第二行输出该项链的字典序最小的表示。
设 \(L =\) 项链长度,则 \(1\leq L \leq 1000000\)。
朴素做法:断环为链,令a=a+a。那么我们就是要在a中匹配一个为b的字串,可以使线性用哈希。
当然考虑到第二问,其实就是要求字符串的最小表示法。我们可以像kmp一样求出a,b的最小表示法后直接比较。
/*
Keyblinds Guide
###################
@Ntsc 2024
- Ctrl+Alt+G then P : Enter luogu problem details
- Ctrl+Alt+B : Run all cases in CPH
- ctrl+D : choose this and dump to the next
- ctrl+Shift+L : choose all like this
- ctrl+K then ctrl+W: close all
- Alt+la/ra : move mouse to pre/nxt pos'
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = l, END##i = r; i <= END##i; ++i)
#define per(i, r, l) for (int i = r, END##i = l; i >= END##i; --i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define ps second
#define pf first
// #define innt int
#define itn int
// #define inr intw
// #define mian main
// #define iont int
#define rd read()
int read(){
int xx = 0, ff = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-')
ff = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
xx = xx * 10 + (ch - '0'), ch = getchar();
return xx * ff;
}
void write(int out) {
if (out < 0)
putchar('-'), out = -out;
if (out > 9)
write(out / 10);
putchar(out % 10 + '0');
}
#define ell dbg('\n')
const char el='\n';
const bool enable_dbg = 1;
template <typename T,typename... Args>
void dbg(T s,Args... args) {
if constexpr (enable_dbg){
cerr << s;
if(1)cerr<<' ';
if constexpr (sizeof...(Args))
dbg(args...);
}
}
#define zerol = 1
#ifdef zerol
#define cdbg(x...) do { cerr << #x << " -> "; err(x); } while (0)
void err() { cerr << endl; }
template<template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(T<t> a, A... x) { for (auto v: a) cerr << v << ' '; err(x...); }
template<typename T, typename... A>
void err(T a, A... x) { cerr << a << ' '; err(x...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
const int N = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 1e18;
const int M = 1e7;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
string a,b;
string getMin(string a){
int n=a.size();
a=" "+a+a;
itn l=1,r=2;
int k=0;
while(r<=n){
k=0;
while(k<n&&a[l+k]==a[r+k])k++;
if(k==n)break;
if(a[l+k]>a[r+k])l+=k,l++;
else r+=k,r++;
if(l==r)r++;
if(l>r)swap(l,r);
}
return a.substr(l,n);
}
void solve(){
cin>>a>>b;
string aa=getMin(a);
string bb=getMin(b);
if(aa==bb){
cout<<"Yes"<<endl<<aa<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
signed main() {
// freopen(".in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".in","w",stdout);
int T=1;
while(T--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
树的最小表示法¶
例题 #1 Subway tree systems¶
【题目描述】
一些主要城市的地铁系统采用树状结构,即在任何两个车站之间,只有一条且仅有一条地铁线路。此外,大多数这些城市都有一个独特的中央车站。想象一下,你是这些城市中的一名游客,你想要探索整个地铁系统。你从中央车站出发,随机选择一条地铁线路,跳上地铁列车。每当你到达一个车站,你就会选择一条你尚未乘坐过的地铁线路。如果在当前车站没有其他要探索的地铁线路了,你就会乘坐第一次到达该车站的地铁线路返回,直到最终你沿着所有的线路都行驶了两次,即每个方向都行驶了一次。在那时,你回到了中央车站。之后,你所记得的探索顺序只是在任何给定时间是否向中央车站更远或更近,也就是说,你可以将你的旅程编码为一个二进制字符串,其中 0 表示乘坐一条地铁线路使你离中央车站更远一站,而 1 表示使你离中央车站更近一站。
【输入格式】
输入的第一行是一个正整数 \(n\),表示接下来要跟随的测试方案的数量。每个测试方案包括两行,每行包含一个长度最多为 \(3000\) 的由字符 '0' 和 '1' 组成的字符串,描述了地铁树系统的正确探索旅程。
【输出格式】
对于每个测试方案,如果两个字符串可以表示相同地铁树系统的探索旅程,则输出 "same";如果两个字符串不能表示相同地铁树系统的探索旅程,则输出 "different"。
翻译来自于:ChatGPT。
/*
Keyblinds Guide
###################
@Ntsc 2024
- Ctrl+Alt+G then P : Enter luogu problem details
- Ctrl+Alt+B : Run all cases in CPH
- ctrl+D : choose this and dump to the next
- ctrl+Shift+L : choose all like this
- ctrl+K then ctrl+W: close all
- Alt+la/ra : move mouse to pre/nxt pos'
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = l, END##i = r; i <= END##i; ++i)
#define per(i, r, l) for (int i = r, END##i = l; i >= END##i; --i)
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define int long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pii pair<int, int>
#define ps second
#define pf first
// #define innt int
#define itn int
// #define inr intw
// #define mian main
// #define iont int
#define rd read()
int read(){
int xx = 0, ff = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-')
ff = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
xx = xx * 10 + (ch - '0'), ch = getchar();
return xx * ff;
}
void write(int out) {
if (out < 0)
putchar('-'), out = -out;
if (out > 9)
write(out / 10);
putchar(out % 10 + '0');
}
#define ell dbg('\n')
const char el='\n';
const bool enable_dbg = 1;
template <typename T,typename... Args>
void dbg(T s,Args... args) {
if constexpr (enable_dbg){
cerr << s;
if(1)cerr<<' ';
if constexpr (sizeof...(Args))
dbg(args...);
}
}
#define zerol = 1
#ifdef zerol
#define cdbg(x...) do { cerr << #x << " -> "; err(x); } while (0)
void err() { cerr << endl; }
template<template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(T<t> a, A... x) { for (auto v: a) cerr << v << ' '; err(x...); }
template<typename T, typename... A>
void err(T a, A... x) { cerr << a << ' '; err(x...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
const int N = 3e5 + 5;
const int INF = 1e18;
const int M = 1e7;
const int MOD = 1e9 + 7;
string a,b;
string s1,s2;
void getMin(string &s)
{
if(s=="01") return;
s=s.substr(1,s.size()-2);
int st=0,cnt=0;
vector<string> v;
v.clear();
for(int i=0;i<s.size();++i)
{
cnt+=(s[i]=='0'?1:-1);
if(!cnt)
{
string ss=s.substr(st,i-st+1);
getMin(ss);
v.push_back(ss);
st=i+1;
}
}
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
s='0';
for(int j=0;j<v.size();++j) s+=v[j];
s+='1';
return;
}
signed main()
{
int t;
scanf("%lld",&t);
while(t--)
{
cin>>s1;
cin>>s2;
s1='0'+s1+'1';
s2='0'+s2+'1';
getMin(s1);
getMin(s2);
if(s1==s2) printf("same\n");
else printf("different\n");
}
return 0;
}